Hyundai and WeRide plan to fuel self-driving with hydrogen in China • ZebethMedia
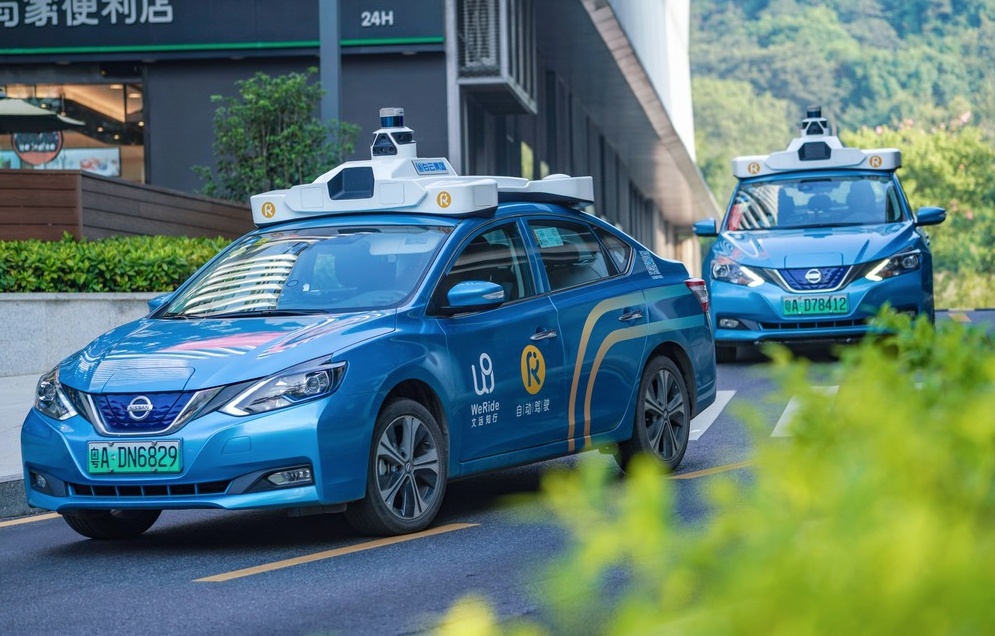
While hydrogen is still relatively niched as a fuel for electric vehicles, a startup in China is jumping ahead to embrace it for autonomous driving scenarios. WeRide, one of the most funded robotaxi operators in China with investors including Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance, said Tuesday it is joining hands with Hyundai to launch a “self-driving hydrogen-powered vehicle pilot zone” in Guangzhou, the southern metropolis where it’s headquartered. The collaboration comes at a time when the research and production of clean hydrogen increasingly becomes a focal point for China, which has been striving to decarbonize its economy. Details are scant from the announcement. It’s unclear when the pilot will kick off, what the scale of the trial is, or what exactly is being powered by hydrogen, which is considered one of the cleanest fuels as it is combined with oxygen to produce just water vapor and energy. But it won’t be surprising to see unmanned hydrogen vehicles roaming about the pilot zone since Hyundai has been betting big on the fuel. Indeed, the announcement says that WeRide, Hyundai, and Hengyun, a Chinese power generation and supply company, will work together to “create demand for the use of hydrogen fuel cell battery in unmanned street cleaning and ride-hailing.” In September last year, Hyundai said it planned to offer hydrogen cell fuel versions for all of its commercial vehicles by 2028. The tie-up with WeRide could expand the use case of its hydrogen products to robotaxis. Hydrogen-fuelled vehicles can recharge within minutes, making them an ideal medium for taxi operations if there’s enough refueling infrastructure. Guangzhou is a natural choice for the experiment given Hyundai has been producing hydrogen fuel cell systems in the city since March 2021. When the facility opened last year, the South Korean auto giant set an annual target to produce “6,500 units, with a goal to gradually expand production capacity in line with Chinese market conditions and central government policies.” China has made a big push to electrify its public transportation. In Shenzhen, the hardware capital of the world, nearly all buses and cabs run on lithium-ion battery packs. While the city has grown quieter with fresher air thanks to the initiative, battery safety and recycling remain big sticking points for the local authorities. Long lines often form at charging stations as it can take hours to fully refuel lithium-ion batteries.