Mason raises $7.5M seed round to scale its no-code commerce engine • ZebethMedia
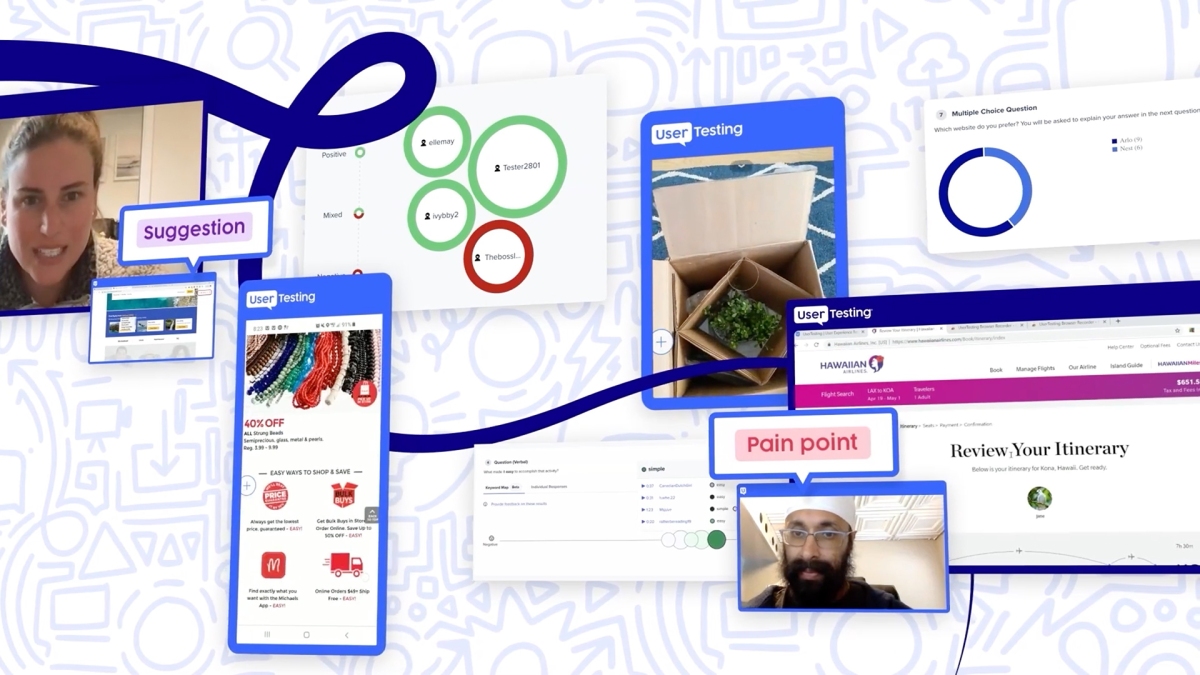
To get a roundup of ZebethMedia’s biggest and most important stories delivered to your inbox every day at 3 p.m. PDT, subscribe here. Hello! And it’s Thursday! We are all waiting with bated breath for the latest installment of “Will Elon Actually Buy Twitter or Will He Squirrel Out of It” — the miniseries of indeterminate length and too many twists and turns to enumerate. Supposedly we’ll learn more tomorrow, but who knows. Also, what is time? And if we all leave Twitter in droves, where will we discuss all of this drama? Our fave little story today was Romain’s, covering these adorable houseplants that can be used as air purifiers. Haje is out tomorrow, so a very happy weekend from him, and Christine will look after all your crunchy needs tomorrow. Adios! — Christine and Haje The ZebethMedia Top 3 Ixnay on the self-drivay: Darrell has had it with all the speculation and calls it: “Truly autonomous vehicles just aren’t going to happen. The evidence pointing to this has been mounting for years now, if not decades, but it’s now tipped the balance to where it’s hard to ignore for a reasoned observer — even one like myself who has previously been very optimistic about self-driving prospects,” he writes. Darrell, we love you, and we hope you’ve never been more wrong. Closing the barn after the horse has bolted: We also have the latest on Elon Musk after his now-famous Twitter office sink video: Amanda reports on his open letter to Twitter advertisers that people have it all wrong about why he is buying the social media giant, but also that Twitter cannot become “a free-for-all hellscape.” Rebecca writes that Musk now says he won’t fire 75% of Twitter’s staff. Avoiding that seller’s tax: Jagmeet writes that sellers on Amazon have to meet certain requirements to sell on the platform, but a startup called Mason is out to change that. The India- and California-based startup secured $7.5 million in fresh funding, led by Accel and Ideaspring Capital, to offer an Amazon-like selling experience but without requiring that “Amazon tax.” Startups and VC There’s a ton of new funds happening all at once, seemingly. Christine reports that Streamlined Ventures, led by Ullas Naik, secured $140 million in new capital commitments for its two newest funds. Haje reports that Human Impact Capital is a new $50 million fund investing in social impact startups, and Mike notes that Paris-based VC Satgana completes the first close of its €30 million fund to back climate tech startups. Meanwhile, there were a bunch of mega-rounds that put the actual investment funds to shame; it’s a weird world when you can’t skim the headline numbers to figure out whether it’s a company raising a round or a new fund closing. We’re collecting a handful of ’em below. 5 tips for launching in a crowded web3 gaming market Image Credits: Chelsea Sampson (opens in a new window) / Getty Images Every online product requires some network effect, but gaming is unique: Without large, loyal and enthusiastic customers, there’s no way to build products that can be monetized. Play-to-earn games (P2E) are particularly susceptible to this problem, which is why “building a game that succeeds in the long term means developing monetization strategies that can weather market ebbs and flows,” says Corey Wilton, co-founder and CEO of Mirai Labs, the gaming studio behind Pegaxy. In this primer for P2E founders, Wilton shares suggestions for how to approach investors, explains why tokens are not a reliable fundraising vehicle and discusses the recent “shift toward Web 2.0 monetization.” Three more from the TC+ team: ZebethMedia+ is our membership program that helps founders and startup teams get ahead of the pack. You can sign up here. Use code “DC” for a 15% discount on an annual subscription! Big Tech Inc. The New York Post had to do some deleting today after it was discovered that someone hacked into both the newspaper’s website and its Twitter account, Zack reports. The article headlines in question were racist and sexually violent in nature, and the newspaper told ZebethMedia that an employee was to blame for the incident but did not go into further details on how it came to that conclusion. Also, our team paid attention to earnings so you didn’t have to. Rebecca has a look into Ford’s third-quarter earnings, which she reports took a $2.7 billion hit related to Argo AI, which we reported yesterday was being shut down. Meanwhile, over at Meta, Amanda writes that Meta had yet another decline in its third-quarter revenue. And now we have three more for you: Googling: Google Cloud has entered web3 territory with a managed blockchain node service by taking on the heavy lifting there so that developers can do their thing, Ron reports. Meanwhile, Manish has details on a $100 million acquisition the search engine giant made in Alter, an AI avatar startup. On an acquisition roll: Ron also reported on yet another Thoma Bravo acquisition. This time, it and Sunstone Partners announced the proposed acquisition of UserTesting for $1.3 billion. The company plans to combine it with its UserZoom, another company Thoma Bravo acquired in 2021. Get your health advice here: YouTube says it will begin certifying channels for licensed health professionals, like doctors, nurses or therapists, who produce health-related content, Ivan writes.