Katakem’s ‘robot chef’ speeds up drug development with reliable chemistry • ZebethMedia
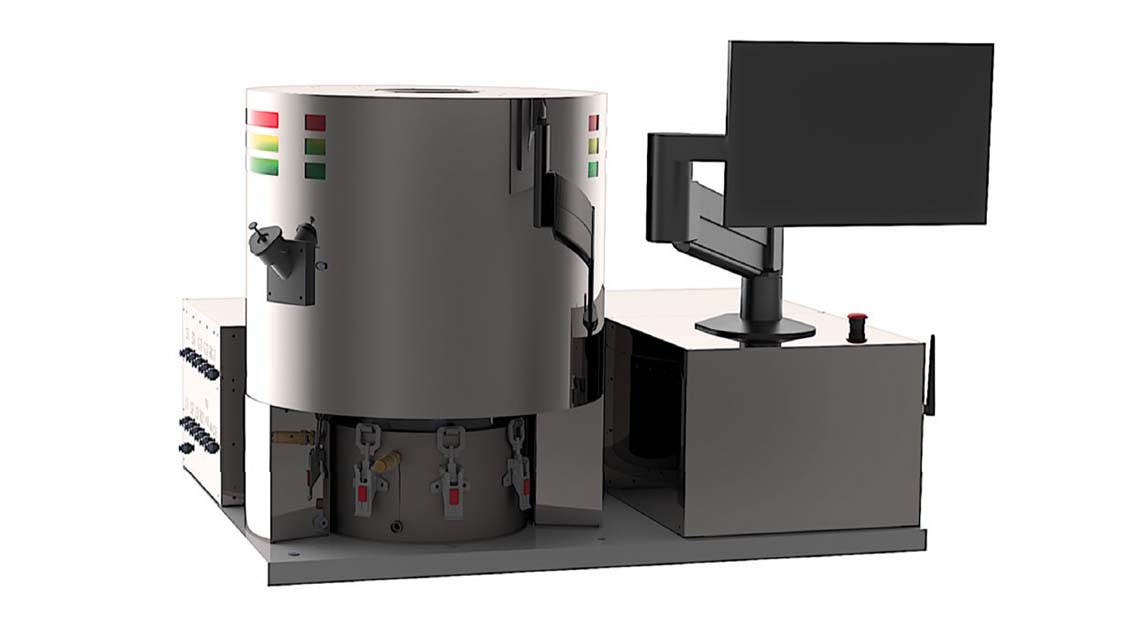
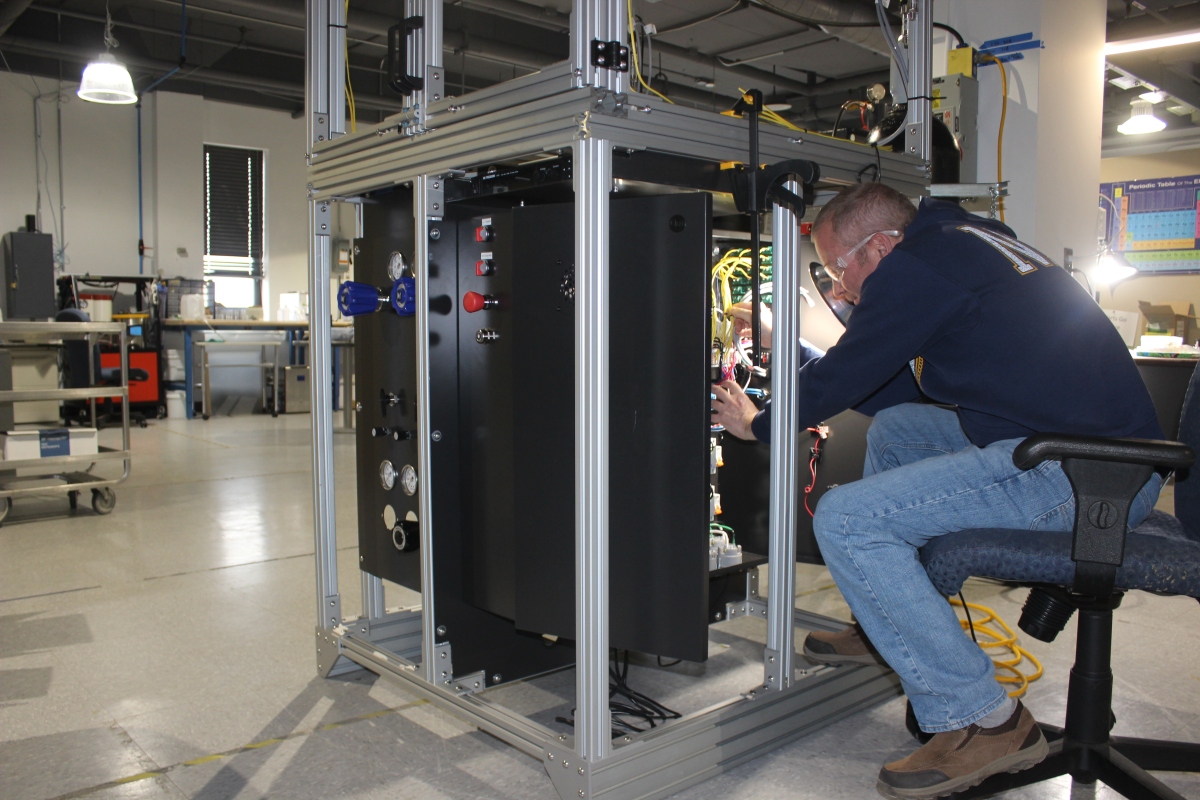
Organic chemist Manuela Oliverio was working on a new drug when he noticed that test results on mice weren’t consistent, because the molecule being administered was always different depending on the chemist who produced it. It occurred to him that automation and robotics could make the drug development process more predictable, and so he founded Katakem, one of the startups in the ZebethMedia Disrupt Battlefield 200. With Katakem, Oliverio aims to develop what he calls a “robot chef” for chemists — a device that makes chemical reactions more consistently reproducible while accelerating the experimental process. He claims that the current prototype, dubbed OnePot, can collect data about chemical processes 150 times every second and automate repetitive, mundane tasks like heating, cooling and mixing different molecules. “The production of a chemical product is strictly regulated and standardized. [But] the development phase between discovery and production is still carried out manually and no significant data is extracted,” Oliverio told ZebethMedia in an interview. “Through data, we can help companies develop new life-saving drugs faster and, of course, this means higher revenues and better margins for them … Data [from OnePot] is reliable, clean and immediately usable.” To Oliverio’s point, drug development today is a lengthy and expensive endeavor. Only about 12% of drugs entering clinical trials are ultimately approved for introduction by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. And estimates of the average R&D cost per drug range from less than $1 billion to over $2 billion, with errors and mistakes adding to the price tag. Katakem developed OnePot over the course of three years, designing both the mechanical and electrical components in-house. The company is seeking chemists to beta test the device, particularly those in corporate and academic settings, to collect data that it plans to use to train an algorithm that can recommend “faster and more sustainable” ways to develop molecules. Image Credits: Katakem Image Credits: Katakem Given the size of the problem — and addressable market — it’s not surprising that Katakem has competition. Automata is also creating a robot to handle basic lab tasks, and it recently raised $50 million to do so. There’s Kebotix, a startup developing AI and robotics tools to expedite the discovery of chemicals, and Artificial, which sells a lab automation platform aimed at life sciences R&D. But while Katakem has the dual challenges of proving its technology works and overcoming rivals, Oliverio isn’t concerned. Based on existing commitments, he expects Katakem’s annual recurring revenue to hit $350,000 by the end of the year and $3 million by the end of 2023. Presumably, those projections assume Katakem finds success with its early customers and demonstrates that OnePot does all the company says it can do. “As our clients — chemical companies — are key to economies, we are not subject to high variability in demand,” Oliverio said. “The robot is ready to be commercialized.” To date, Calabria, Italy-based Katakem has raised €1.3 million ($1.27 million) in capital from undisclosed seed investors, according to Crunchbase data.