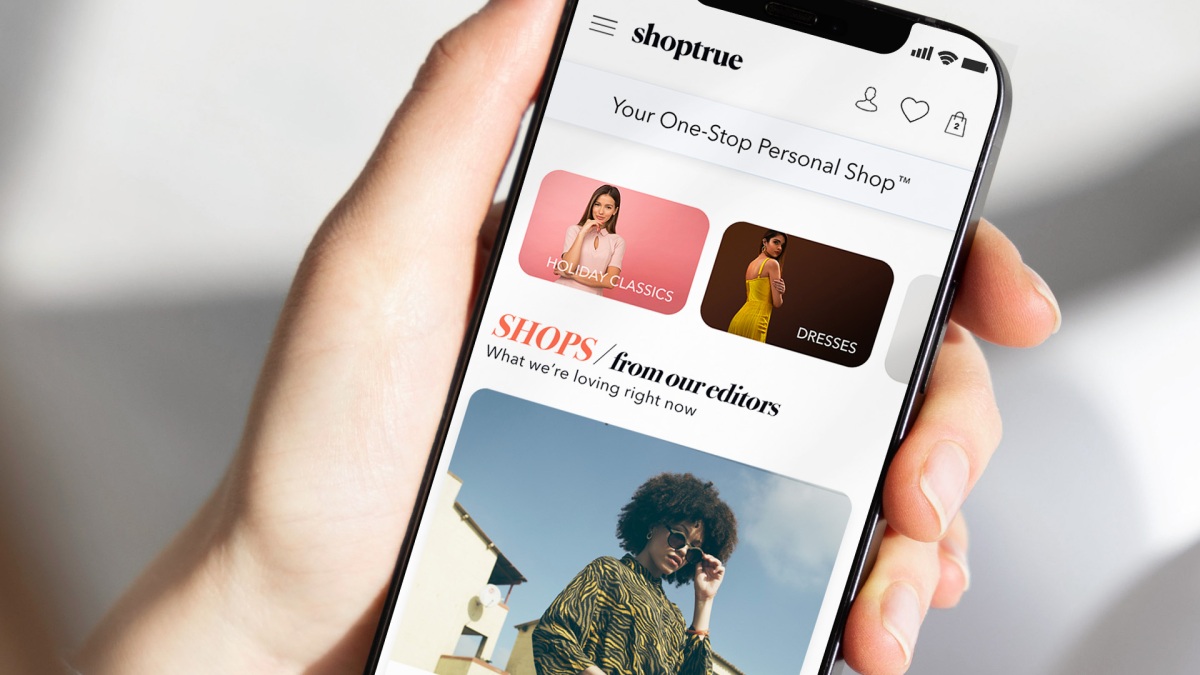
An A.I.-powered online fashion marketplace, Shoptrue, is launching its website into beta today with plans for a public release early next year. The site blends artificial intelligence and personalized recommendations with taste-driven shopping, the company says, which helps give users a source for style inspiration as well as the ability to create and share outfit ideas with others. Rather than the typical algorithmic approach such as Amazon, which ranks items based on a strong sales history, Shoptrue is A.I.-driven and continually improves its product recommendations based on purchase behaviors and user engagement. That way, users can have more say on what items they see on their curated feeds. The site offers a “One Stop Personal Shop” for the user, which gives fashion suggestions based on their style preferences. Users can eliminate the items they dislike and purchase items directly on Shoptrue through its unified checkout process. Romney Evans, the founder of Shoptrue, told ZebethMedia, “Instead of being a top-down recommendation system, where the user is passive, it’s putting the user in the driver’s seat, back into personalization, giving them the controls.” Image Credits:Shoptrue Shoptrue’s individualized shopping experience begins with an onboarding quiz, which includes questions about your style personality, favorite brands, and color preferences– similar to other personalized e-commerce sites, like Stitch Fix. Shoptrue users can then browse a large selection of merchandise from over 2,000 merchants that range from high-end brands like Alexander Wang, Christian Louboutin, Gucci, and Dolce & Gabbana, to affordable retailers like Ross, Kohls, Nordstrom Rack, H&M, and Forever 21. There are also “Shops,” or collections created by Shoptrue’s team of editors, that users can explore for inspiration. For instance, the “Girl’s Night Out” lookbook features trendy miniskirts, strappy heels, tanks, graphic pants, and handbags. Users will soon get to create and share their own Shops, Shoptrue says. Peer-generated Shops will also roll out when Shoptrue officially launches out of beta. Image Credits: Shoptrue Shoptrue will also soon launch the ability to pre-filter size and fit specifications, so shoppers only see the products in stock that are in their size. This is a natural step for the company as Evans is also the co-founder of True Fit, the personalization company that built a data platform to help online shoppers find the correct sizes for apparel and footwear. Within the next year or so, Shoptrue users will be able to create a True Fit profile that helps determine what size they are for specific items, Evans explained to ZebethMedia. As Shoptrue evolves, the company plans to add features based on customer feedback. “We invite shoppers everywhere to join us on this journey. It will take time, but today begins our rollout of an exciting stream of innovation and distinctive experiences that will make it easy to get only what you love. We aspire to delight shoppers and earn their trust as we improve their shopping experience every month and every quarter through innovation, trial and error, and by listening to their feedback,” Evans said. With the launch of Shoptrue, Evans has brought on a team of technology and fashion experts, including Brandon Holley, a Condé Nast veteran with over 25 years of experience in fashion, and former Netflix data scientist John Lashlee. Holley is also the founder and CEO of Everywear, a technology platform that’s now incorporated into Shoptrue and helps with custom recommendations and foreseeing purchase behaviors. The startup raised $6 million in seed funding in 2021 to help build, test, and launch its beta. Investors included Signal Peak Ventures, Pelion Venture Partners, and Peterson Ventures. The company expects to raise additional funding in 2023. Founder of Shoptrue Romney Evans (left), Chief Fashion Officer Brandon Holley (middle), VP of Data Science John Lashlee (right) Shoptrue’s business model is typical for online marketplaces. When a user completes a transaction with a merchant via Shoptrue, the company takes a commission on those sales. Shoptrue declined to share the commission range but said it was standard for most fashion marketplaces. (Note that Poshmark’s and ASOS Marketplace’s commission is 20%.) There is no fee for brands to participate on Shoptrue. Social media platforms like Instagram and TikTok are becoming increasingly responsible for influencing the shopping habits of young consumers—especially Gen Z. Shoptrue hopes that Gen Z and Millenials will feel empowered to share their Shops and fashion favorites on social media, get help from Shoptrue’s style experts and find other users and influencers that use the platform. Shoptrue’s launch is another example of how AI technology is transforming the e-commerce industry. In June, Pinterest acquired the AI-powered shopping platform The Yes, which builds a personalized fashion feed and continually learns about a user’s style as they shop. Pinterest said the deal would help the company become the home for taste-driven shopping. “We are making it easier for people to find only the things they’re going to love, and then give them the tools to organize and share their style POV with the world,” Shoptrue’s Chief Fashion Director Brandon Holley said in an announcement. “Anybody’s shop has the potential to set off a chain reaction of fashion inspiration that can surprise and delight you from any direction.”